What are the odds of HIV in Ghana?
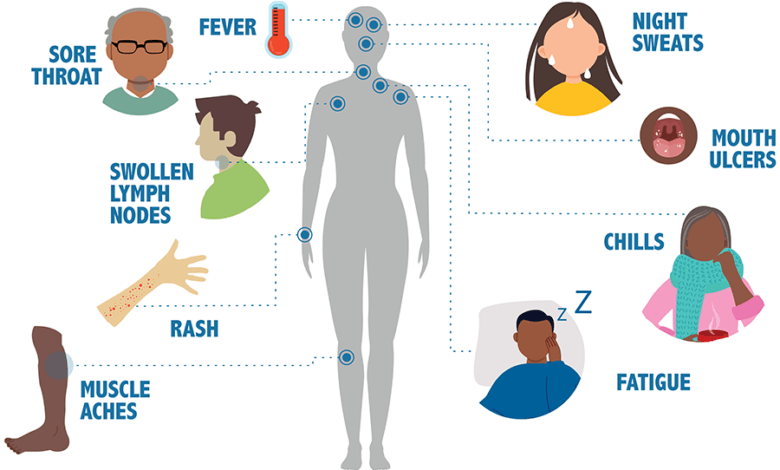
WHO states that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an infection that targets the body’s immune system, in particular the CD4 cells, which are white blood cells. A person’s resistance to opportunistic infections like tuberculosis and fungal infections, severe bacterial infections, and several malignancies is weakened as a result of HIV’s destruction of these CD4 cells, a particular lymphocyte.
By encouraging other immune cells to combat infection, such as macrophages, B lymphocytes, and CD8 T lymphocytes (CD8 cells), CD4 T lymphocytes (CD4 cells) aid in the coordination of the immunological response. HIV damages CD4 cells, weakening the immune system. WHO advises getting tested for HIV for everyone who may be at risk. People who are more likely to contract HIV should look for comprehensive and efficient services for HIV prevention, testing, and treatment.
The 5 Mental Health Benefits of Daily Exercise
Self-tests and straightforward, cost-effective, and quick diagnostic procedures can both be used to identify HIV infection. The 5Cs—consent, confidentiality, counselling, accurate results, and connection to treatment and other services—must all be adhered to by HIV testing services.
HIV is typically a sexually transmitted infection that spreads through contact or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and vaginal secretions. An infected mother can pass her infection to her unborn child non-sexually through breast milk, her blood, or her vaginal discharge while she is pregnant. HIV can be found in these physiological fluids as both free virus particles and as a virus inside infected immune cells. Research has revealed that if the HIV-positive partner continuously maintains an undetectable viral load, HIV cannot be transmitted through condom-free sexual contact between same-sex or opposite-sex partners.
According to HIV.gov, there is currently no effective HIV treatment, and the human body cannot get rid of HIV. Therefore, if you have HIV, you will always have it.
Antiretroviral therapy, or ART, an effective HIV treatment option, is fortunately available. HIV medications have the ability to significantly lower the viral load, another name for the amount of HIV in the blood, if taken as directed. The term for this is viral suppression. A person is said to have an undetected viral load if their viral load is so low that a typical lab is unable to detect it. People with HIV can live long, healthy lives and won’t spread the virus to their partners if they take their HIV medications as directed and achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load.
Benefits of Assure Soap: Radiant and Healthy Skin with Neem, Tulsi & Pudina
Additionally, there are effective ways to avoid contracting HIV through sex or drug use, such as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a drug that people who are at risk for contracting HIV take to avoid contracting HIV through sex or injecting drugs, and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), a drug that HIV-positive people must take within 72 hours of potential exposure to stop the virus from establishing a foothold.
Recent headlines regarding antiretroviral medications that have been detained at the port since July are particularly concerning because the objective is to stop the spread of HIV infection by 2030.
According to a press release from the Ghana Health Service, tax waivers on the antiretroviral drugs were issued on time, but the batch’s high volume necessitated additional resources, which would be secured by October 13 to clear the drugs.
It’s crucial to take your HIV medication in pill form every day and exactly as directed.
This is crucial since skipping doses might lead to HIV changing its form, which will prevent your medicine from working. The term for this is drug resistance. HIV can develop resistance to both your medicine and untried, comparable drugs. Your options for effective HIV treatment are so limited. HIV strains that are resistant to treatment can also spread to other people.
Your viral load will remain low, and your CD4 cell count (the number of white blood cells that fight infection) will remain high if you take your HIV medication every day in the precise way that your doctor instructs you to. If you occasionally miss a dose, you give HIV the chance to spread quickly. Your immune system can be compromised as a result, and you might get sick.
This indicates that HIV-positive people are more at risk when antiretroviral medications are scarce.
The hope that these pharmaceuticals will be released from the port on the scheduled day is crucial.