5 Common Diseases Among the Elderly and How to Prevent Them

Aging is a beautiful journey, but it also comes with health challenges that often go unnoticed until they cause serious damage. Many seniors experience diseases that could have been prevented early with the right lifestyle, monitoring, and family support.
Recommended: AKA Killers Finally Face Justice in SA Court
This in-depth guide explores five common diseases among older adults, their symptoms, risk factors, and practical ways to prevent them. Whether you’re caring for a parent, grandparent, or planning for your own healthy aging, this article provides life-changing insights.
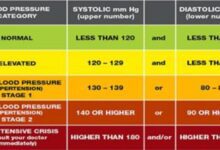
1. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Why It’s Common Among the Elderly
As people age, arteries naturally stiffen, making it harder for the heart to pump blood. Combined with lifestyle factors like poor diet and low activity, hypertension becomes extremely common among seniors.
Symptoms
Hypertension is called a “silent killer” because most people have no symptoms until major damage occurs.
When symptoms appear, they may include:
Severe headaches
Dizziness
Blurred vision
Chest pain
Fatigue
Complications
Untreated high blood pressure can lead to:
Stroke
Heart attack
Kidney failure
Vision loss
Prevention
Reduce salt intake
Exercise at least 20–30 minutes daily
Maintain a healthy weight
Avoid excessive alcohol and smoking
Check blood pressure regularly
2. Diabetes (Type 2 Diabetes)
Why It Affects Many Seniors
Aging slows down metabolism and reduces insulin sensitivity. Combined with poor diet and lack of movement, diabetes becomes almost inevitable for many older adults.
Symptoms
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Fatigue
Slow wound healing
Blurred vision
Complications
Nerve damage
Kidney damage
Heart disease
Vision problems
Prevention
Adopt a low-sugar, balanced diet
Increase fiber intake
Maintain regular physical activity
Reduce carbohydrate-heavy meals
Conduct routine blood sugar tests
3. Arthritis
What Makes Arthritis Common in Old Age
Years of joint wear-and-tear cause inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common forms among seniors.
Symptoms
Joint pain
Stiffness
Swelling
Complications
Loss of mobility
Increased risk of falls
Chronic pain
Prevention
Engage in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, cycling
Maintain a healthy weight
Stretch regularly
Use ergonomic chairs and shoes
Take anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric & omega-3s
4. Dementia (Including Alzheimer’s Disease)
Why Dementia Is a Growing Problem
As the brain ages, memory cells weaken. Genetics, lifestyle, and chronic diseases also contribute.
Symptoms
Memory loss
Difficulty recognizing people
Confusion
Mood changes
Trouble speaking or understanding
Complications
Severe cognitive decline
Loss of independence
Behavioral problems
Prevention
While dementia has no cure, prevention can significantly reduce risk:
Keep the brain active (puzzles, reading, learning new skills)
Engage in regular physical exercise
Eat brain-healthy foods (nuts, berries, fish)
Avoid smoking and excessive drinking
Manage hypertension, cholesterol, and diabetes
Recommended: The 5 Mental Health Benefits of Daily Exercise
5. Osteoporosis
Why Seniors Are at Risk
Bones naturally lose density with age. Women, especially after menopause, are more vulnerable.
Symptoms
Often silent until a fracture occurs. Warning signs include:
Back pain
Loss of height over time
Fragile bones
Complications
Hip fractures
Spinal fractures
Long-term disability
Prevention
Take calcium and vitamin D-rich foods
Exercise, especially weight-bearing activities
Avoid smoking
Reduce alcohol use
Bone density tests for early detection
General Prevention Tips for All Elderly Diseases
To maintain long-lasting health:
Eat a nutrient-rich diet
Stay hydrated
Sleep 7–8 hours
Reduce stress
Maintain regular hospital check-ups
Stay socially active to boost mental well-being
Good health in old age is not luck, it’s intentional lifestyle choices and early detection.